Climate and science reporter
Data journalist
 Getty Images
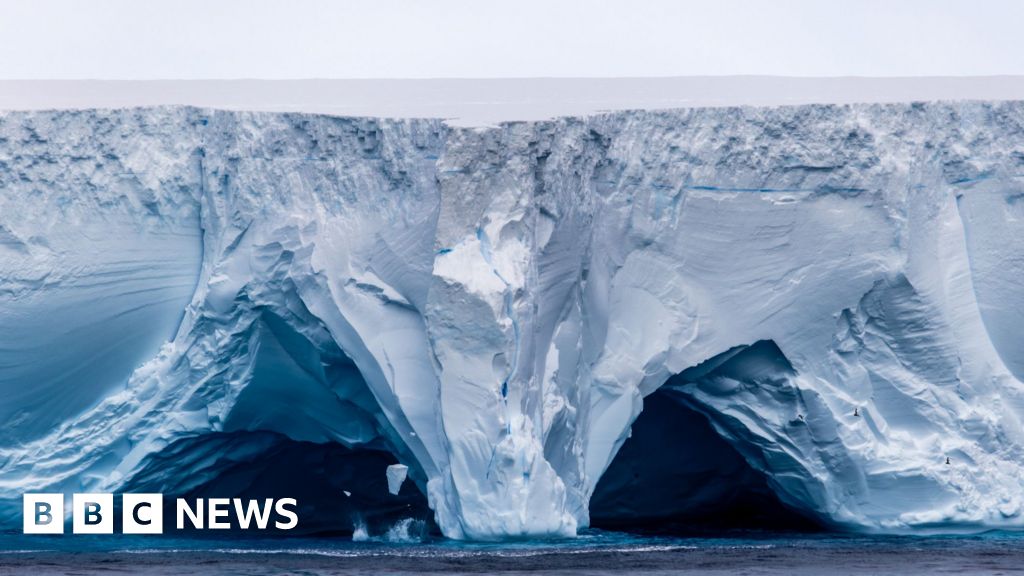
Getty ImagesThe world’s largest iceberg is on a collision course with a remote British island, potentially putting penguins and seals in danger.
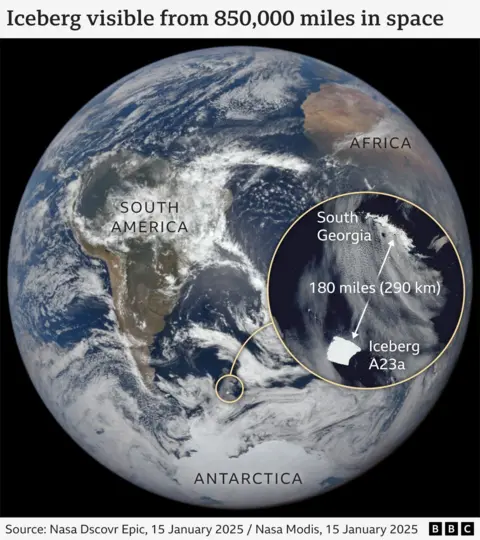
The iceberg is spinning northwards from Antarctica towards South Georgia, a rugged British territory and wildlife haven, where it could ground and smash into pieces. It is currently 173 miles (280km) away.
Countless birds and seals died on South Georgia’s icy coves and beaches when past giant icebergs stopped them feeding.
“Icebergs are inherently dangerous. I would be extraordinarily happy if it just completely missed us,” sea captain Simon Wallace tells BBC News, speaking from the South Georgia government vessel Pharos.
 BFSAI
BFSAIAround the world a group of scientists, sailors and fishermen are anxiously checking satellite pictures to monitor the daily movements of this queen of icebergs.
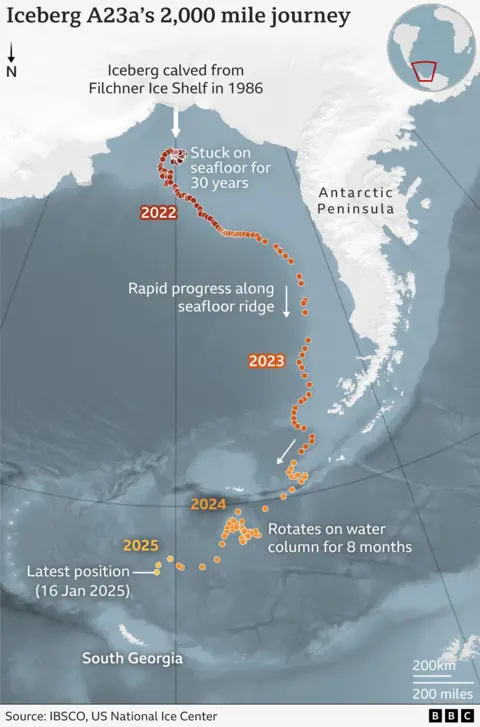
It is known as A23a and is one of the world’s oldest.
It calved, or broke off, from the Filchner Ice Shelf in Antarctica in 1986 but got stuck on the seafloor and then trapped in an ocean vortex.
Finally, in December, it broke free and is now on its final journey, speeding into oblivion.
The warmer waters north of Antarctica are melting and weakening its vast cliffs that tower up to 1,312ft (400m), taller than the Shard in London.
It once measured 3,900 sq km, but the latest satellite pictures show it is slowly decaying. It is now around 3,500 sq km, roughly the size of the English county of Cornwall.
And large slabs of ice are breaking off, plunging into the waters around its edges.
A23a could break into vast segments any day, which may then hang around for years, like floating cities of ice cruising uncontrollably around South Georgia.
This isn’t the first huge iceberg to threaten South Georgia and Sandwich Islands.
In 2004 one called A38 grounded on its continental shelf, leaving dead penguin chicks and seal pups on beaches as massive ice chunks blocked their access to feeding grounds.
The territory is home to precious colonies of King Emperor penguins and millions of elephant and fur seals.
“South Georgia sits in iceberg alley so impacts are to be expected for both fisheries and wildlife, and both have a great capacity to adapt,” says Mark Belchier, a marine ecologist who advises the South Georgia government.
Sailors and fisherman say icebergs are an increasing problem. In 2023 one called A76 gave them a scare when it came close to grounding.
“Chunks of it were tipping up, so they looked like great ice towers, an ice city on the horizon,” says Mr Belchier, who saw the iceberg while at sea.
Those slabs are still lingering around the islands today.
“It is in bits from the size of several Wembley stadiums down to pieces the size of your desk,” says Andrew Newman from Argos Froyanes, a fishing company that works in South Georgia.
“Those pieces basically cover the island – we have to work our way through it,” says Captain Wallace.
The sailors on his ship must be constantly vigilant. “We have searchlights on all night to try to see ice – it can come from nowhere,” he explains.
A76 was a “gamechanger”, according to Mr Newman, with “huge impact on our operations and on keeping our vessel and crew safe”.
 Simon Wallace
Simon WallaceAll three men describe a rapidly changing environment, with glacial retreat visible year-to-year, and volatile levels of sea ice.
Climate change is unlikely to have been behind the birth of A23a because it calved so long ago, before much of the impacts of rising temperatures that we are now seeing.
But giant icebergs are part of our future. As Antarctica becomes more unstable with warmer ocean and air temperatures, more vast pieces of the ice sheets will break away.
Before its time comes to an end though, A23a has left a parting gift for scientists.
A team with the British Antarctic Survey on the Sir David Attenborough research vessel found themselves close to A23a in 2023.
The scientists scrambled to exploit the rare opportunity to investigate what mega icebergs do to the environment.
 Tony Jolliffe/BBC
Tony Jolliffe/BBCThe ship sailed into a crack in the iceberg’s gigantic walls, and PhD researcher Laura Taylor collected precious water samples 400m away from its cliffs.
“I saw a massive wall of ice way higher than me, as far as I could see. It has different colours in different places. Chunks were falling off – it was quite magnificent,” she explains from her lab in Cambridge where she is now analysing the samples.
Her work looks at what the impact the melt water is having on the carbon cycle in the southern ocean.
 Getty Images
Getty Images“This isn’t just water like we drink. It’s full of nutrients and chemicals, as well as tiny animals like phytoplankton frozen inside,” Ms Taylor says.
As it melts, the iceberg releases those elements into the water, changing the physics and chemistry of the ocean.
That could store more carbon deep in the ocean, as the particles sink from the surface. That would naturally lock away some of the planet’s carbon dioxide emissions that contribute to climate change.
Icebergs are notoriously unpredictable and no-one knows what exactly it will do next.
But soon the behemoth should appear, looming on the islands’ horizons, as big as the territory itself.
















Leave a Reply